Water Quality
There were potential sightings of cyanobacteria on 9/18/25, but we were unable to collect samples for testing to confirm.
Why Fall Turnover Can Trigger Cyanobacteria Sightings
As summer ends, Unity Pond goes through a natural process called fall turnover.
What is turnover?
All summer long, the lake sits in layers:
Warm water on top (where people swim and fish).
A middle layer (where the temperature drops quickly and mixing stops).
Cold water at the bottom (cut off from wind and air).
In late September, the surface cools and becomes heavy enough to sink. Wind then stirs the lake from top to bottom, breaking down those layers.
Why does this matter for algae?
During summer, the bottom waters lose oxygen. Without oxygen, phosphorus and other nutrients can be pulled from the sediments.
When turnover happens, those nutrients are mixed up into the surface waters where algae and cyanobacteria can use them to grow.
This “nutrient boost” can cause short-lived patches of cyanobacteria, sometimes seen as green streaks or scums.
Should we be worried?
Turnover events don’t always lead to harmful blooms, but cyanobacteria sightings can happen this time of year.
These patches are often brief, wind-driven, and disappear as cooler weather and shorter days set in.
The safest approach is to avoid contact with visible scums, especially for pets.
Key Point: Fall turnover is a natural reset for the lake, but it can temporarily stir up nutrients that feed cyanobacteria. That’s why we sometimes see surface patches just as the lake is beginning to recover its clarity.
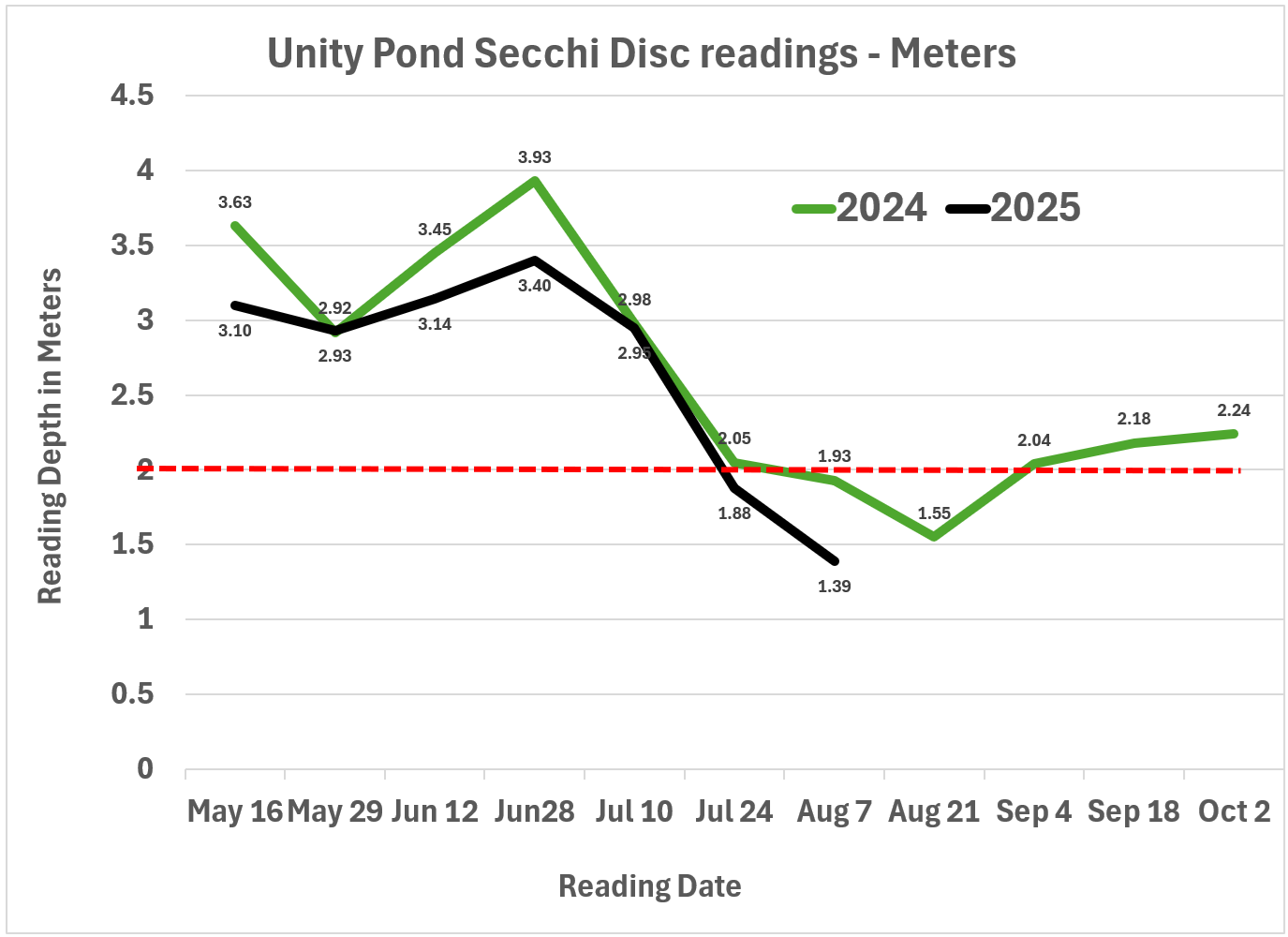
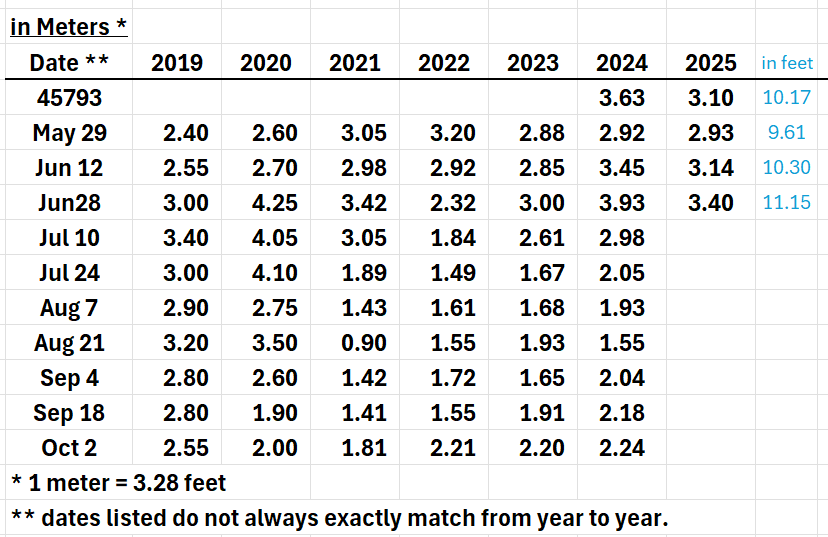
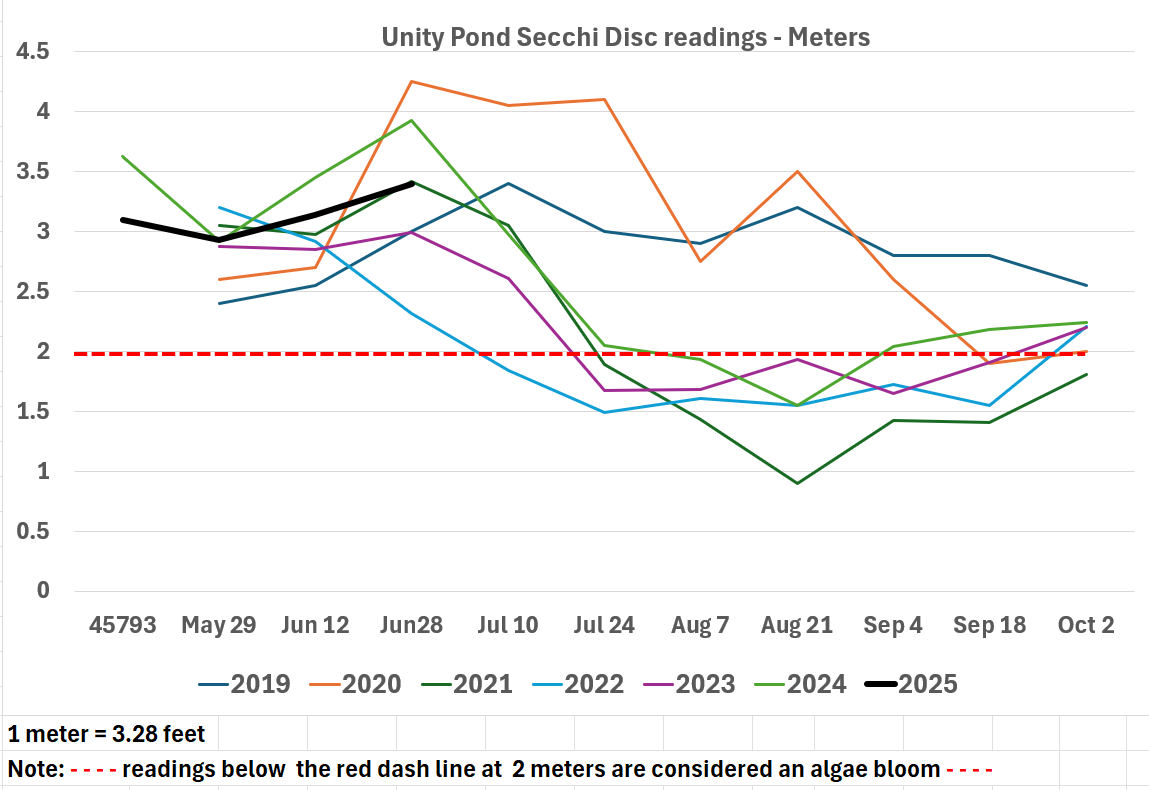
Water Clarity UPDATE – Unity Pond (Secchi Depth in Meters)
Current Reading 9/19/2025 - 2.79 m
Clarity Trend - Improving over the last 4 Weeks
Aug 22: Clarity was at its lowest point of the season at 1.39 m, well below the 2.0 m threshold. Conditions at this time were highly impaired and consistent with a bloom.
Sept 5: A significant rebound occurred, with clarity improving to 2.33 m. This represented the first return above the impairment line since late July.
Sept 19: Clarity continued to strengthen, reaching 2.79 m.
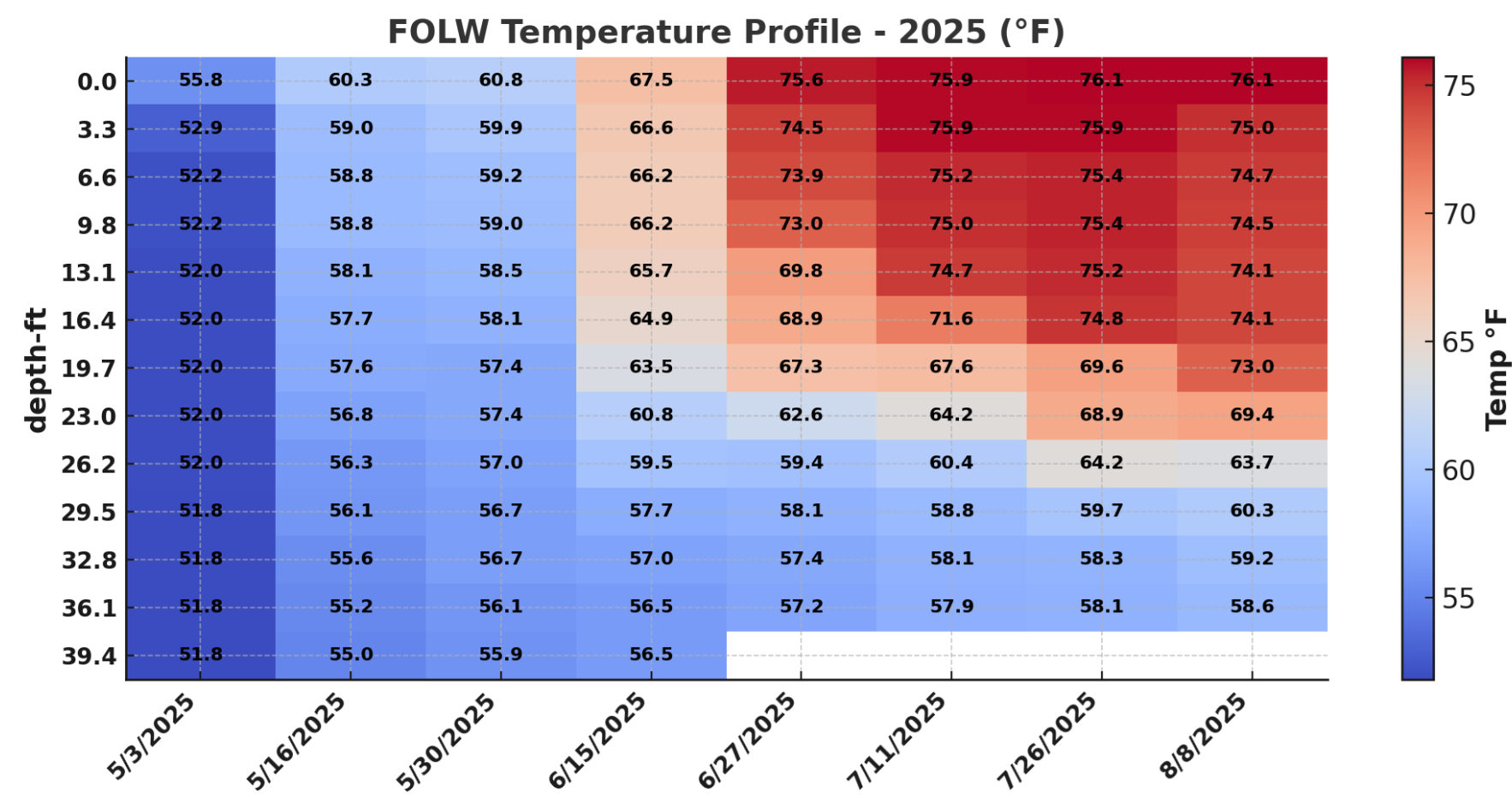
2025 Temperature Profile
FOLW Temp Summary — Unity Pond 2025
Surface temperatures rose from ~55 °F in early May to the mid-70s by late July, then cooled to near 68 °F in September.
The mixed layer extended to about 15 ft by midsummer.
A thermocline developed from 15–25 ft in June and persisted through August with sharp gradients.
Deep water below 30 ft remained stable near 52–54 °F all season.
Key Point: Strong stratification prevented oxygen mixing to the bottom, setting up hypolimnetic depletion and nutrient release that can fuel blooms during turnover.
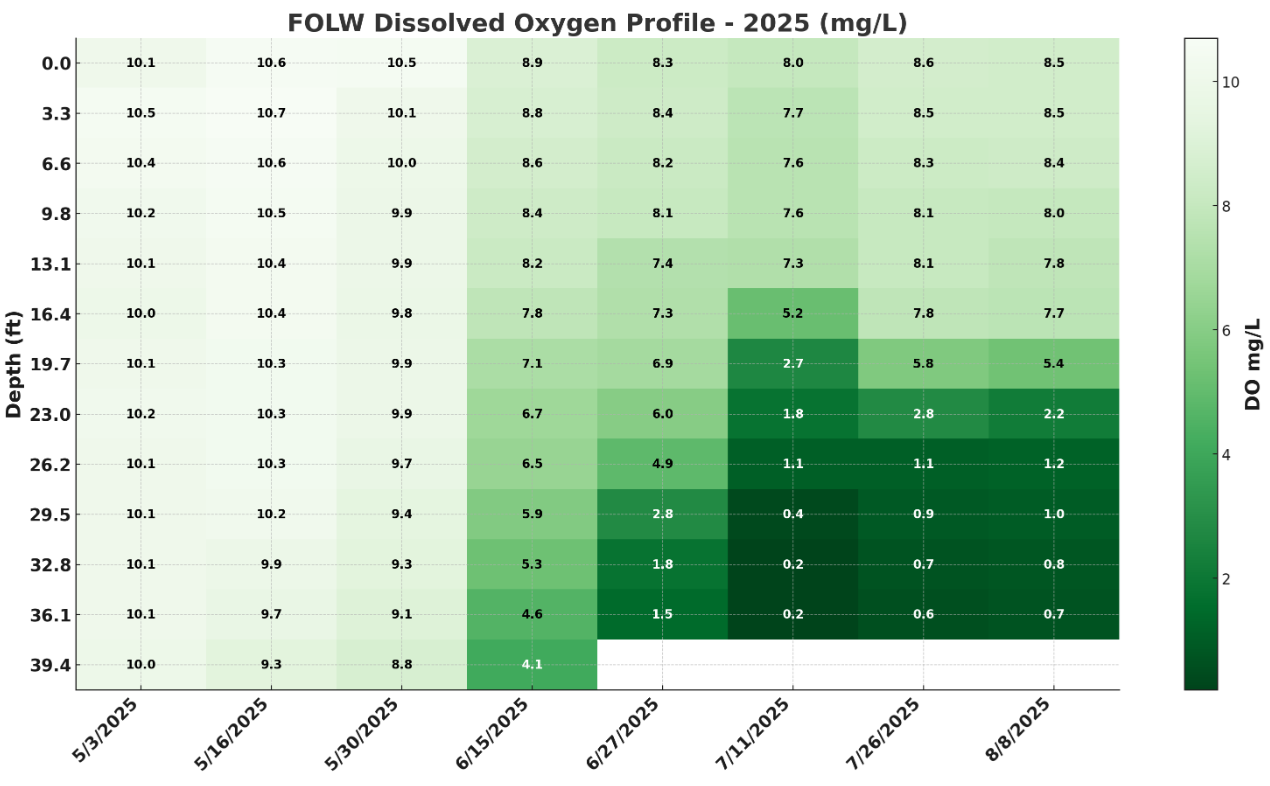
2025 Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
Unity Pond Dissolved Oxygen – 2025 Season Summary
Throughout the summer, Unity Pond showed the classic pattern of oxygen loss in the deeper waters:
Spring (May–June): Oxygen levels were healthy from top to bottom, above 8–10 mg/L, supporting fish throughout the lake (down to 12 m / ~40 ft).
Mid-Summer (July–August): As the lake became layered, the bottom waters (below ~7 m / 23 ft) lost oxygen rapidly. By July, deep areas dropped to near-zero, leaving fish habitat limited to the upper 0–6 m (0–20 ft).
Late Summer (August): The oxygen “dead zone” at the bottom persisted, while surface waters stayed well-oxygenated.
September Turnover: By September 19, the lake began mixing. This turnover brought low-oxygen deep water upward, causing oxygen levels to fall throughout the water column (surface DO dropped below 8 mg/L).
Why this matters
During turnover, nutrients that had built up in the oxygen-poor bottom water were released into the surface. This mixing may explain the cyanobacteria sightings reported September 18th, when short-lived green patches appeared on the pond.
Past Water Quality Reports are Below
Water Clarity UPDATE – Unity Pond (Secchi Depth in Meters)
Current Reading 9/5/2025 - 2.33 m
Best clarity: ~3.4 m (~11.2 ft) in mid-June
Lowest clarity: ~1.39 m (~4.6 ft) on Aug 8 & Aug 22
Recent trend: Water clarity dropped sharply in July, reached a low in early August, but recovered earlier than in 2024, climbing back to ~2.33 m (~7.6 ft) by Sept 5
Key Point: The midsummer bloom reoccurred, but 2025 rebounded more quickly, likely aided by cooler August nights (mean temp ~1.2 °F lower than 2024), limited rainfall (~1.7" vs. ~3" normal), and early September mixing.
9/5/2025 Temperature Profile Update
FOLW Temperature Summary (9/5/2025)
Surface Temperature: ~70 °F, cooling steadily since mid August
Mixed Layer Extent: From surface down to ~26 ft
Thermocline Range: Between ~26 ft and ~33 ft, where temperature drops rapidly
Deep Water Stability: Below ~33 ft, temperatures remain stable around 61 to 62 °F
Key Point:
The lake remains moderately stratified, but signs of early September mixing are appearing, helping blend some mid-depth waters and setting up conditions for oxygen recovery at depth.
9/5/2025 Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Update
FOLW DO Summary (2025)
Upper Layer (0–13 ft): Oxygen levels stayed strong all season, generally 7–10 mg/L, providing good habitat for fish and aquatic life.
Mid-Depth (16–23 ft): Oxygen depletion began by mid-July, dropping as low as ~2.7 mg/L at 20 ft. Recovery started by late August, rising back above 6 mg/L.
Deep Layer (26–39 ft): Severe hypoxia (<1 mg/L) developed from mid-July through mid-August. By Sept 5, oxygen levels rebounded significantly (up to ~6.1 mg/L at 26 ft), showing early signs of fall mixing.
Key Point:
A prolonged midsummer oxygen deficit created an environment supporting an internal phosphorus release. However, earlier September mixing in 2025 is restoring oxygen more quickly, which helped drive the faster Secchi rebound and may limit late-season algal growth compared to 2024.
Water Clarity UPDATE – Unity Pond (Secchi Depth in Meters)
Current Reading 8/22/2025 - 1.39 m
Best clarity: ~3.4 m (~11.2 ft) in mid-June
Lowest clarity: ~1.39 m (~4.6 ft) on Aug 8 & Aug 22
Recent trend: Water clarity declined significantly from June to early August.
Key Point: Reduced Secchi depth indicates increased algal growth and reduced light penetration, consistent with the warm surface temps and declining oxygen at depth.
8/22/2025 Temperature Profile Update
FOLW Temperature Summary (8/22/2025)
Surface Temperature: ~72.3 °F, cooling from last week
Mixed Layer Extent: From surface down to ~26 ft
Thermocline Range: Between ~26 ft and ~33 ft, where temperature drops rapidly
Deep Water Stability: Below ~33 ft, temperatures remain stable around 59 to 60 °F
Key Point:
The lake remains strongly stratified, preventing mixing between the warm, oxygen-rich upper waters and the colder deep waters.
8/22/2025 Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Update
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Summary (8/22/2025)
Upper Layer (0–10 ft): ~7.7 mg/L — healthy oxygen levels
Mid-Depth Layer (10–20 ft): ~6.9 mg/L — moderately well-oxygenated
Deep Layer (>26 ft): ~0.8 mg/L — Very low oxygen - anoxic conditions
Key Point:
We have improved DO readings at the 20 to 23 ft levels with the positive effects of wind and wave action. Because of strong stratification, oxygen replenishment from surface waters is not reaching the lower depths. Deep waters remain oxygen-depleted, increasing the risk of phosphorus release from sediments — a process that can fuel algal blooms as mixing occurs later in the fall.
Water Clarity UPDATE – Unity Pond (Secchi Depth in Meters)
Current reading (Aug 8, 2025): 1.39m, the seasonal low.
Trend: Water clarity in 2025 continues to be lower than 2024 for nearly all dates since May 16.
Comparison to 2024: On the same date last year (closest comparable – Aug 7, 2024), clarity was 1.93 m, meaning this year’s clarity is about 25% lower.
Implication: Conditions indicate a sustained bloom period, with visibility well below the 2.0 m threshold used to define significant algal bloom conditions.
Outlook: Unless weather or mixing events occur, clarity is likely to remain low through mid-to-late August before any improvement.
8/8/2025 Temperature Profile Update
Temperature Profile Summary – FOLW Temp Chart (Aug 8, 2025)
Key Point: Strong summer stratification is in place, preventing the mixing of oxygen from the upper layers with the lower layer. This isolation contributes to oxygen depletion in deep water and increases the likelihood of internal phosphorus loading and resulting Algal Bloom.
8/8/2025 Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Update
Dissolved Oxygen Summary – FOLW DO Chart (Aug 8, 2025)
Upper Layer (0–20 ft): Healthy oxygen levels (≥5 mg/L), suitable for fish and aquatic life.
Mid-Depth (23–26 ft): Severe oxygen depletion (<2.5 mg/L).
Deep Layer (>26 ft): Near-anoxic conditions (~1 mg/L or less).
Key Point:
With no mixing, oxygen cannot reach the lower layers, leading to hypolimnetic (Lower Level) oxygen depletion. Low oxygen at the sediment-water interface can cause phosphorus to be released from sediments, fueling algal blooms.
As of July 26, 2025, the Secchi disk reading dropped to 1.88 meters (6.2 feet)—a clear indication of an algal bloom now underway in Unity Pond.
Readings below 2 meters (the dotted red line) indicate a bloom
Lake Temperature Trends – Spring to Summer 2025
Lake Temperature Trends – Spring to Summer 2025
From early May through late July 2025, Unity Pond experienced steady warming of surface and deeper waters. Surface temperatures (0 meters) rose from 13.2°C (55.8°F) on May 3 to 24.5°C (76.1°F) by July 26. At 6 meters, temperatures increased from 11.1°C (52.0°F) to 20.9°C (69.6°F), showing significant warming well below the surface.
Key observations:
Thermal stratification — the layering of warm water over cooler, deeper water — was well established by mid-June.
Temperatures exceeded 20°C (68°F) at depths down to 5–6 meters by late July, limiting mixing and oxygen distribution.
These stagnant, warm conditions set the stage for harmful algal blooms, which thrive in such environments.
Continuous monitoring of temperature patterns supports water quality management and bloom forecasting.
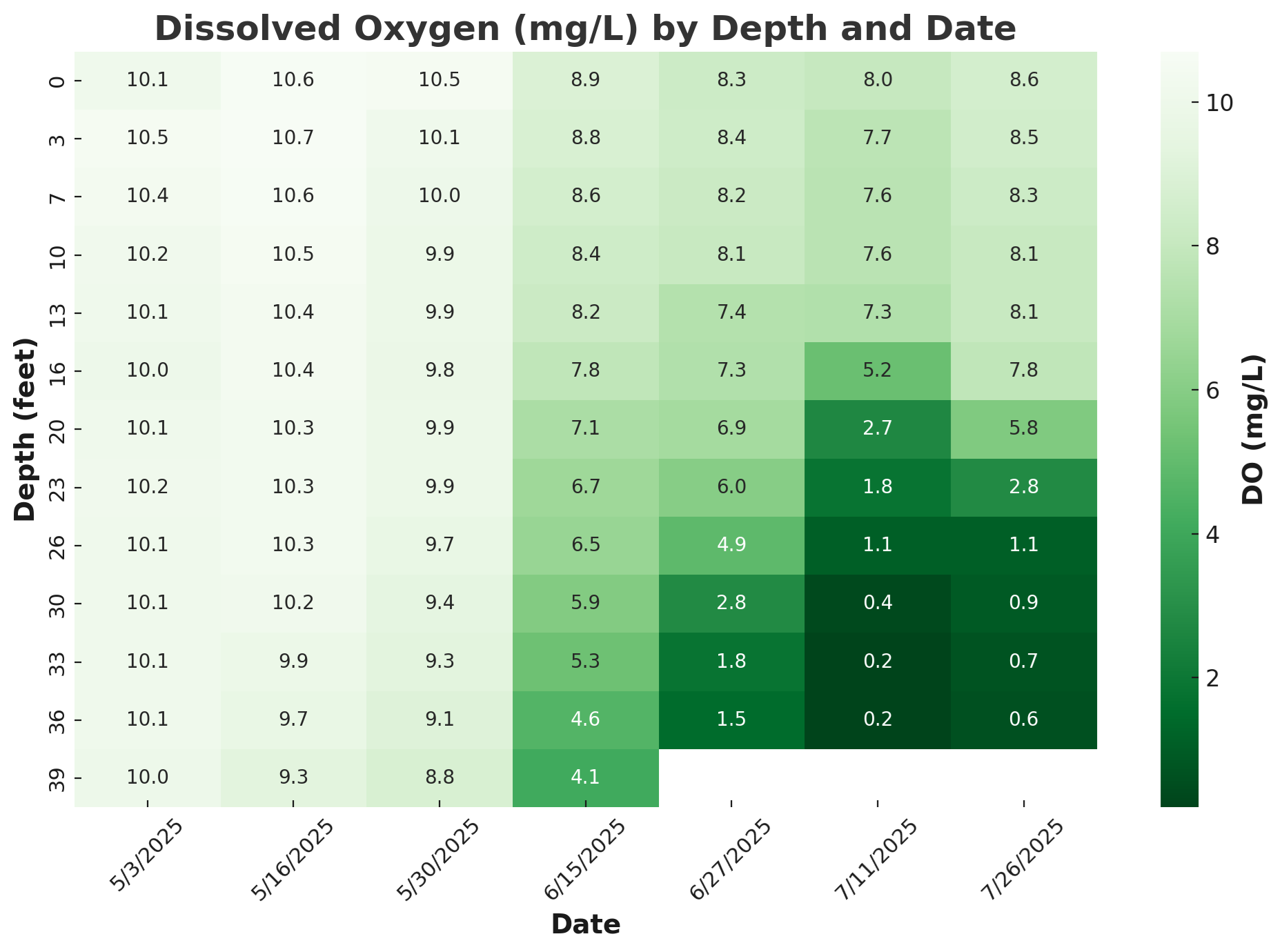
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Levels – Spring to Summer 2025
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Levels – Spring to Summer 2025
Oxygen levels in Unity Pond remained high and well-distributed throughout the water column in early spring, with concentrations around 10 mg/L at all depths. However, as surface temperatures rose and the lake stratified:
Oxygen began to decline rapidly below 6 meters, starting in mid-June.
By early July, DO levels fell to hypoxic conditions (below 2 mg/L) at depths greater than 7 meters.
By late July, oxygen was nearly depleted (≤1 mg/L) at depths 9 meters and deeper, creating anoxic conditions in bottom waters.
These changes can lead to the release of nutrients from sediments and promote harmful algal blooms.
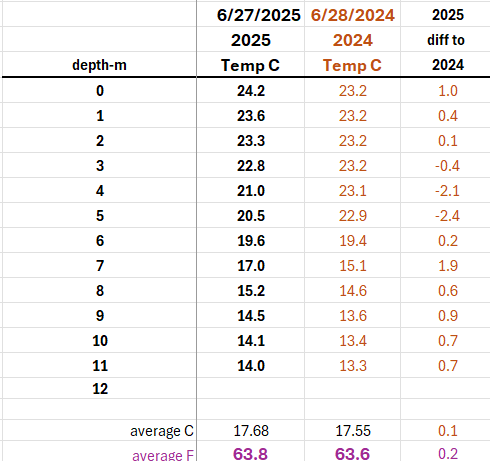
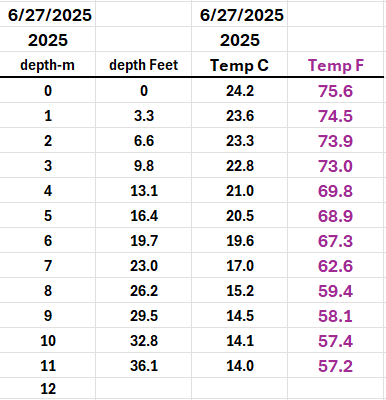
Secchi Disc Update 6/27/2025
My apologies to those who attended the Let’s Make it Clean Not Green meeting on June 26, 2025. I incorrectly reported the June 15 Secchi reading as 3.41 meters; the correct reading was 3.14 meters.
The latest Secchi Disc reading taken on June 27, 2025, shows 3.40 meters (approximately 11 feet), indicating an improvement in water clarity.
Temperature Update
The lake continues to warm, and the surface temperature of the lake has increased by 1°C compared to the same time last year. While we've experienced a few hot days with temperatures over 90°F, we've also had some cool nights dipping into the low 50s. The lake is warming, but on average the temperature increase is only 0.1°C compared to last year for the.
Please note: Temperature readings at the 12-meter (39.4 ft) depth are no longer being recorded, as the lake’s depth has dropped to 37.6 ft at the Midas Point—the deepest location in the lake.
Here are the 6/27/2025 temperatures readings with depth converted from meters to feet and temp converted from C to F.
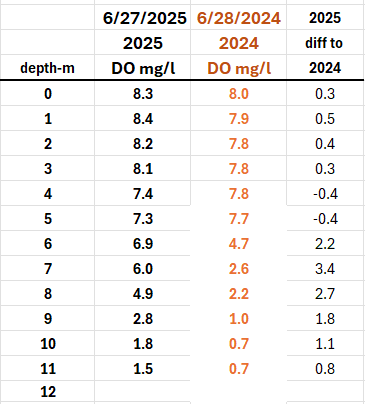
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Update
Dissolved Oxygen (DO) levels continue a gradual seasonal decline as expected (warmer water holds less oxygen) but encouragingly remain higher this year compared to the same period last year.
On June 27, 2025, DO readings at the 9, 10, and 11-meter depths are above 1.0 mg/L, which is an improvement. In 2024, these same depths had already dropped to 1.0 mg/L or below, a condition known as anoxia—where oxygen levels are too low to support most aquatic life. This is critical because when DO levels fall below 1 mg/L, phosphorus bound to iron in lakebed sediments is released into the water column. This "internal loading" of phosphorus acts like fertilizer and can fuel algae blooms.
The key takeaway:
DO above 1 mg/L at the lake bottom slows phosphorus release from sediments.
Why This Matters
DO < 1 mg/L = Anoxia = Phosphorus Release from Iron in lake bottom sediment
DO > 1 mg/L = Less Internal Phosphorus Loading
This is where Alum Treatment plays a vital role. Unlike iron, aluminum binds to phosphorus in a stable form, even under anoxic conditions. So, even as DO drops later in the season, the phosphorus remains locked up, reducing the risk of algal blooms.
Water temperature significantly impacts lake water quality by affecting the amount of dissolved oxygen, nutrient levels, stratification patterns, and the growth of algae and other aquatic organisms, with warmer temperatures generally leading to decreased dissolved oxygen, increased algal blooms, and potential disruption of the ecosystem balance, ultimately impacting the overall health of the lake
Water Temperature readings for 2024
Dissolved Oxygen readings for 2024
Dissolved oxygen (DO) is crucial to a lake's health because it is essential for the survival of all aquatic organisms, including fish, plants, and invertebrates, as they need oxygen to breathe, making it a key indicator of water quality and the ability of a lake to support life; low DO levels (below 2.0 mg/l) can lead to stress, disease, and even fish kills if significantly depleted
Microcystins
Microcystins are a family of toxins produced by cyanobacteria, a type of blue-green algae, that can cause serious illness in humans and death in animals
Friends of Lake Winnecook tested for Microcystins in 2023 and 2024, the results were negative for the presence of Microcystins.
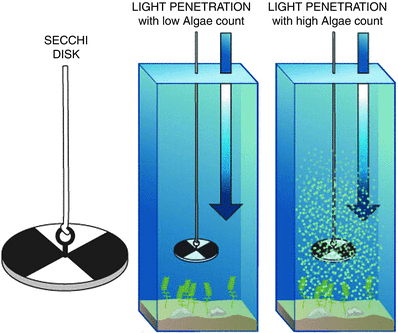
Secchi Disk
A Secchi Disc Reading is recorded when the Disc is no longer visible